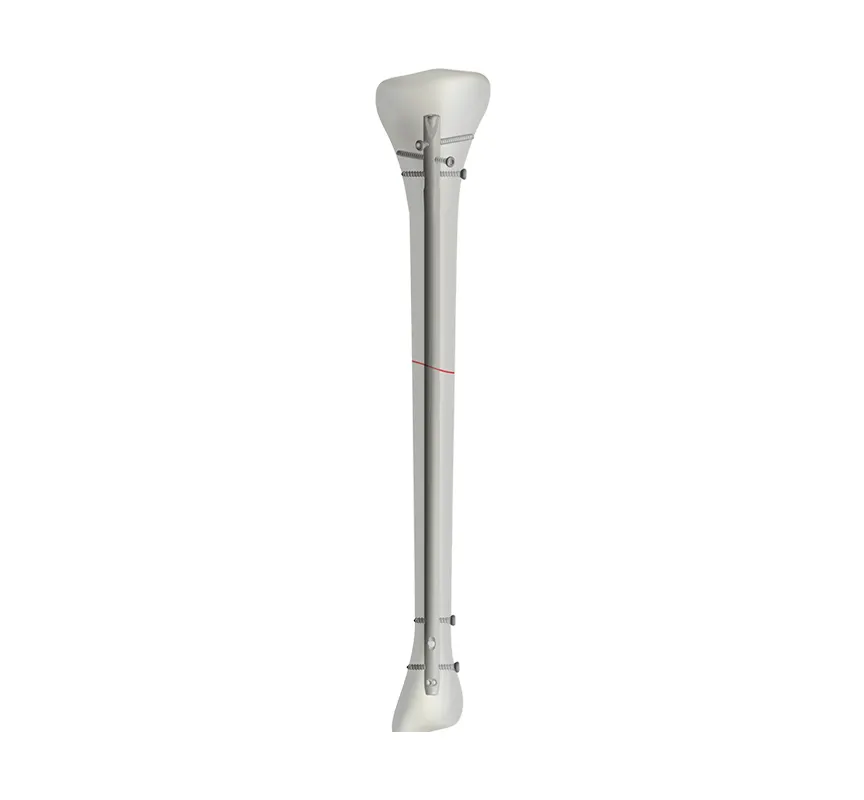
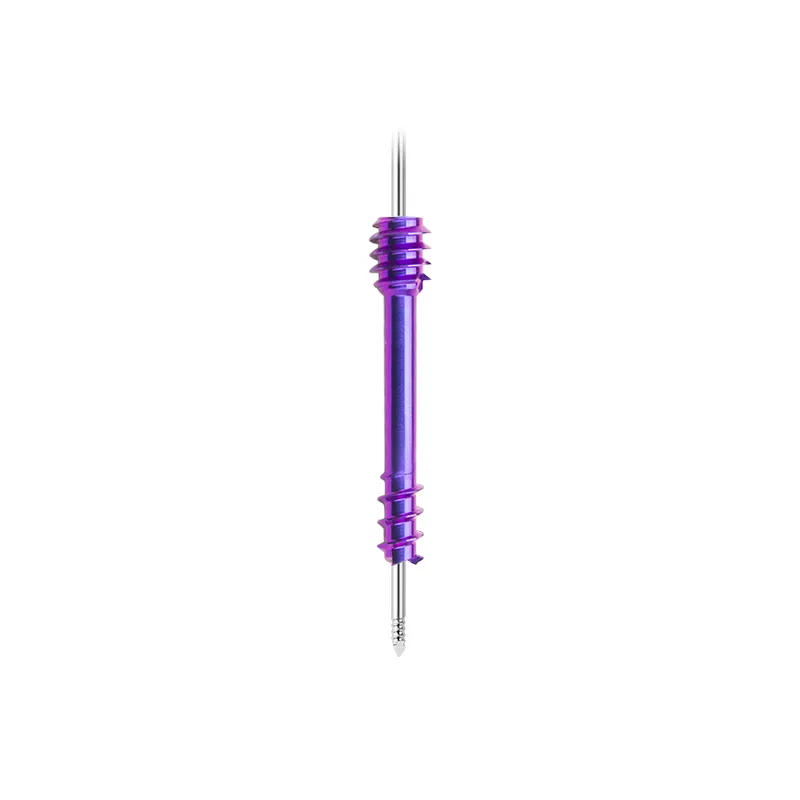
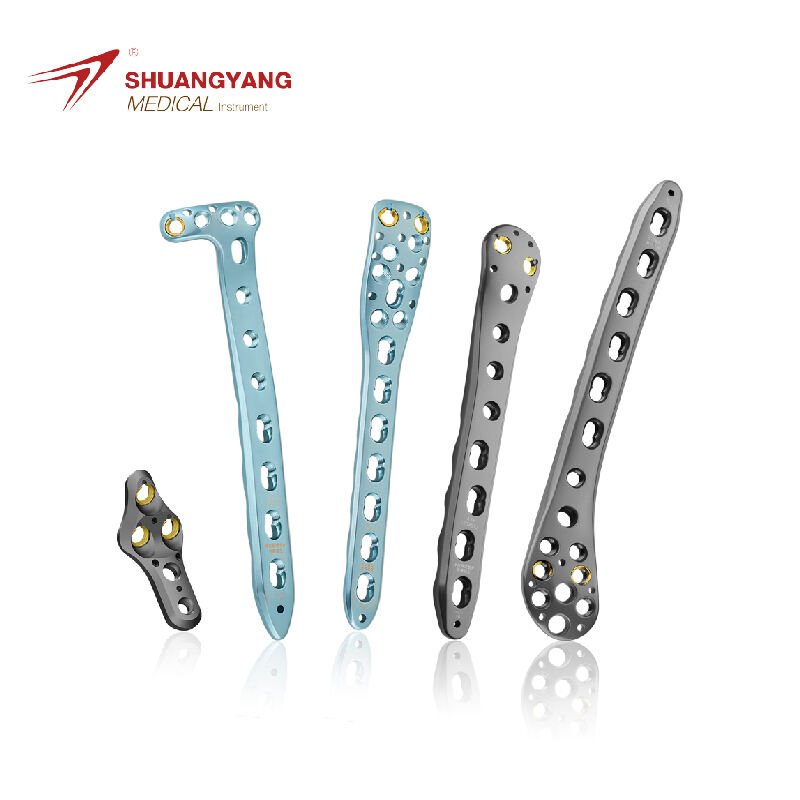
Choosing the Right Maxillofacial Titanium Plate for Your Needs
h2 { margin-top: 26px; margin-bottom: 18px; font-size: 24px !important; font-weight: 600; line-height: normal; } h3 { margin-top: 26px; margin-bottom: 18px; font-size: 20px !important; font-weight: 600; line-height: ...
View More
 EN
EN
 FR
FR
 ES
ES
 AR
AR